EAR DRUM INFECTION OR PERFORATED EAR DRUM OR HOLE IN THE EAR DRUM.
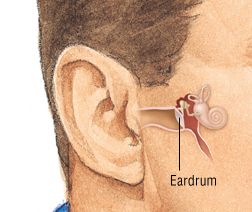
Internal structure of ear include eardrum, is a thin membrane that separates your ear canal (the part that is open to the outside) from your middle ear. The eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane, it is the apparatus of hearing. Sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate. This includes the process of converting the sound waves into an impulse that travels into the brain, where it is recognized as sound.
 |
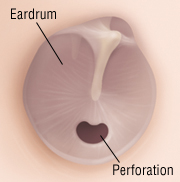
The eardrum is very delicate, thin and can be torn (perforated) easily, most often by an infection of the middle ear (otitis media) other than that, by other types of trauma, including:
- Inserting an object, such as a cotton swab or toothpick, too far into the ear
- A very loud noise, such as an explosion
- Trauma to the head, such as any accidents, skull fracture
- A blow to the ear
- Trauma to the ear caused by changes in air pressure (barotraumas), such as during a plane flight or scuba diving
Symptoms
Symptoms of a perforated eardrum include:
- Earache or sudden relief of an earache
- Hearing loss in the affected ear
- Bleeding or fluid discharge from the ear canal
- Ringing noise in the ear
The complications of hearing loss depends on the size of the perforation and what caused it. Trauma to the ear or head could injure the middle ear, inner ear or both, and could cause severe hearing loss. If an explosion has torn the eardrum, it may have ringing in the ears (tinnitus) for several days, as well as hearing loss. If the perforated eardrum becomes infected, the hearing loss may be worsen.
 |
Diagnosis
The doctor will look into the ear using an instrument called an otoscope to see if the eardrum is torn, and also will test your hearing. If the doctor suspects you have a ruptured eardrum but cannot see the perforation easily, then this may confirm the diagnosis by blowing pressurized air into the ear using a special machine.
Expected Duration
Although the perforated eardrums heal in a few weeks. Some take up to two months. Exposure to water or further trauma can slow the healing. Also, if the ear gets infected during the healing phase, the perforation is less likely to close on its own. Larger tears, or tears that do not heal on their own, may require surgery.
Prevention
There are several steps you can take to prevent a perforated eardrum:
- Reduce the risk of a perforated eardrum by preventing middle ear infections. To help prevent infections, minimize certain environmental conditions – exposure to tobacco smoke and allergens – and avoid direct contact with people with a cold or flu. Children also can get immunizations against two common bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae) that cause middle ear infections.
- Do not insert cotton swabs into the ear canal during cleaning because this can tear the eardrum.
- If an object gets into your ear, have it removed by the doctor to minimize the risk of ear injury. Don't try to take out the object yourself unless you can see it clearly, it is soft and you can remove it easily.
- Have all infections treated promptly to avoid complications.
Treatment
If the hole is small, The doctor may allow it to heal on its own, and may have you take antibiotics to prevent infection while the eardrum heals. Keep water out of the injured ear, and avoid blowing your nose, which can cause pressure changes in the ear and disrupt healing.
Some holes may be patched in the office of an otolaryngologist (ear, nose and throat doctor). A thin paper patch is placed over your eardrum in combination with a chemical that encourages the eardrum to heal.
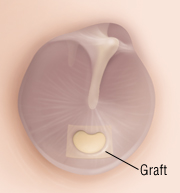 |
If the eardrum has not healed after two months, The doctor may recommend a surgery called tympanoplasty, which involves using tissue from another area to patch the eardrum. This is usually an outpatient procedure and has a high success rate.
While the ear is healing from the surgery, keep the ear dry by using cotton balls covered with Vaseline to protect the eardrum from water during showers or baths. Also, avoid blowing the nose, which can damage the healing tissue. Warm compresses, such as a warm, damp washcloth, or a heating pad can relieve some discomfort. The doctor also may prescribe pain-relieving medication or recommend that you use over-the-counter pain medications.
Comments
Post a Comment